Solutions
- Home
- Solutions

Peter Adams
co-founder of company
Scientific partners
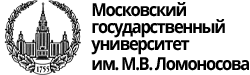





Collaboration MSTU "STANKIN" with AVK
The joint work of MSTU “STANKIN”, as a center of knowledge and competencies, and AVK, as a polybranch industrial partner of the integrator, allows to effectively identify current industry requests for automation equipment and new technologies, quickly develop, test and implement solutions that meet the most modern industrial requirements and allowing to implement advanced rates of technological development.
The collaboration includes:
- Industrial Automation and Robotics Center;
- Engineering and testing laboratory;
- Retraining programmes for the training of RTC repairers and operators.
Center for Industrial Automation and Robotics:
- Development of multifunctional universal robotic platforms of collaborative type for industrial application in shipbuilding and ship repair industries, as well as in oil and gas processing and mining industries, industrial and infrastructure construction industries;
- Development and modernization of automated lines for manufacturing industries;
- Adaptation of technological impact equipment for use in robotic complexes;
- Development of systems for machine quality control of work performed, including with the use of artificial intelligence technologies;
- Development and implementation of retraining programs for specialized personnel
Comprehensive retraining programs for training specialists, adjusters and operators of RTC
- Design and application of RTC;
- Operation and maintenance of RTC.
Adoption rates of industrial robotics in the World and Russia
Relevance of the application of robotics systems for delivery of technological impact
- Improving the quality of coatings due to computer precision and intelligent algorithms of implementing impact;
- Reduction of involvement of manual labor;
- High productivity;
- The ability deliver impact to hard-to-reach, high-altitude and hazardous to human health and life objects;
- Reduction of material consumption;
- Ensuring the continuity of the work process;
- Automated quality control;
- Ensuring repeatability of technological processes;
- Remote monitoring of processes.
In the structure of the R&D Center, an engineering and testing laboratory has been established to develop various modes of technological impact for mobile and stationary robotic platforms:
- Search work to determine, standardize and optimize surface treatment modes;
- Determination of the potential for implementation and economic effect of RTС application;
- Debugging of process charts for specific technical requirements;
- Testing of impact technologies.
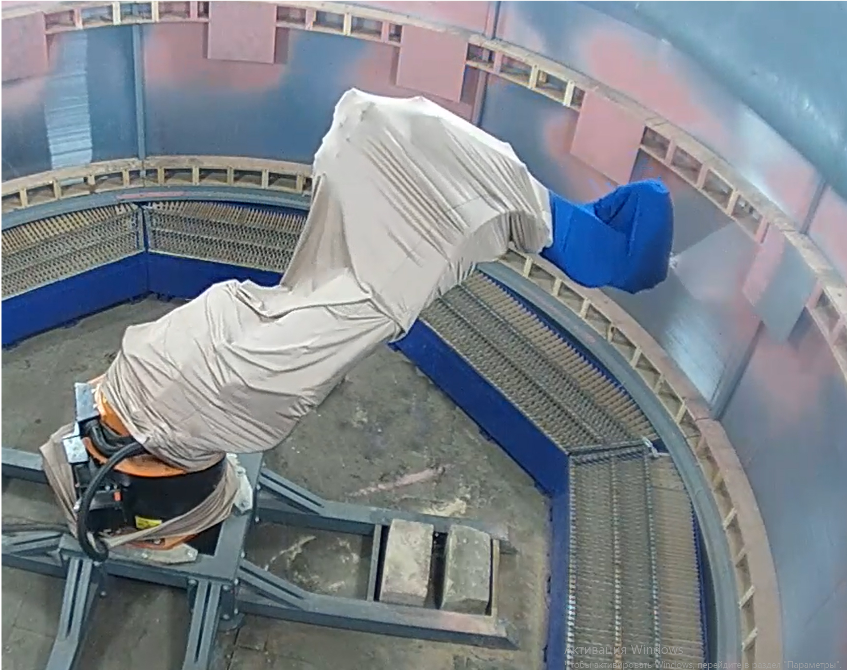

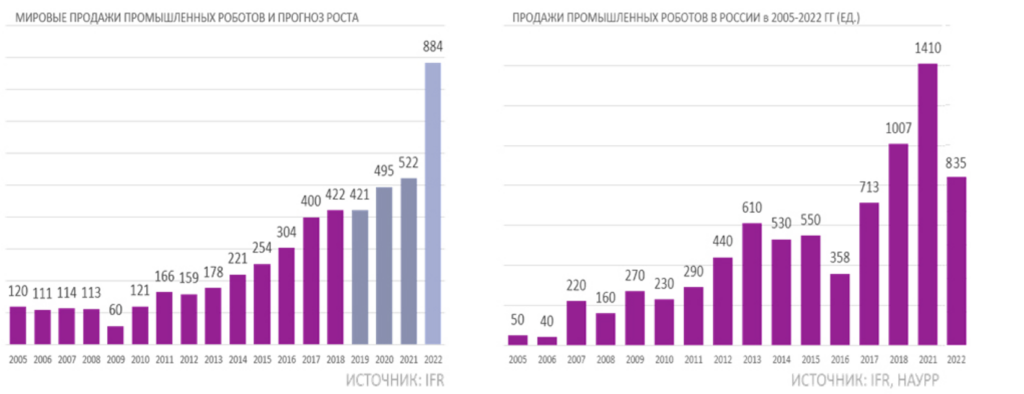
The R&D Center specialists have developed a software package for setting the trajectory of movement, speed and cyclicity of impact.
- The software package implements a digital twin of the test bench, fully synchronized with the full-scale bench based on an industrial manipulation robot.
The developed package generates the software code for controlling the manipulator on the digital twin of the stand, which allows:
- Carry out the preparation and conduct of a series of experiments in parallel;
- Ensure the repeatability of experiments;
- Perform precise adjustments of the positioning and movement parameters of the working tool;
- Document experiments while preserving parameters and trajectories.
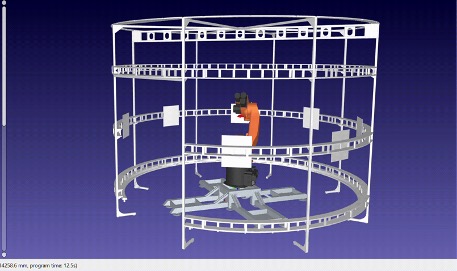
A software package for testing various options for the trajectory of manipulators and the chassis of the RTС using the capabilities of the ROS2 software framework for developing robots
- The software provides generation of control actions on the drives in the manipulators and platforms depending on the desired trajectory, speed and other parameters of the movement of the process equipment located on the flange of the manipulator.
- The illustration shows the visualization of the trajectory control of the RTC flange in the RVIZ environment of the ROS2 package.
A unique mathematical apparatus has been developed for modeling the parameters of applying protective coatings and calculating the operating modes of the RTC.
Modeling allows:
- Optimize the trajectories and algorithms of the RTC movement by processing time;
- IImprove the functional qualities of coatings by achieving homogeneity and specified thickness parameters;
- Ensure material savings;
- Calculate optimal processing modes for materials with different mechanical and chemical properties.







